- algorithm-reading
- leetcode/lintcode题解/算法学习笔记
- 1. Part I - Basics
- 2. Data Structure
- 3. Basics Sorting
- 4. Basics Misc
- 5. Part II - Coding
- 6. String - 字符串
-
7.
Integer Array - 整型数组
- 7.1. Remove Element
- 7.2. Zero Sum Subarray
- 7.3. Subarray Sum K
- 7.4. Subarray Sum Closest
- 7.5. Product of Array Exclude Itself
- 7.6. Partition Array
- 7.7. First Missing Positive
- 7.8. 2 Sum
- 7.9. 3 Sum
- 7.10. 3 Sum Closest
- 7.11. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
- 7.12. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
- 7.13. Merge Sorted Array
- 7.14. Merge Sorted Array II
- 7.15. Median
-
8.
Binary Search - 二分搜索
- 8.1. Binary Search
- 8.2. Search Insert Position
- 8.3. Search for a Range
- 8.4. First Bad Version
- 8.5. Search a 2D Matrix
- 8.6. Find Peak Element
- 8.7. Search in Rotated Sorted Array
- 8.8. Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
- 8.9. Search a 2D Matrix II
- 8.10. Median of two Sorted Arrays
- 8.11. Sqrt x
- 8.12. Wood Cut
- 9. Math and Bit Manipulation - 数学技巧与位运算
-
10.
Linked List - 链表
- 10.1. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
- 10.2. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
- 10.3. Remove Duplicates from Unsorted List
- 10.4. Partition List
- 10.5. Two Lists Sum
- 10.6. Two Lists Sum Advanced
- 10.7. Remove Nth Node From End of List
- 10.8. Linked List Cycle
- 10.9. Linked List Cycle II
- 10.10. Reverse Linked List
- 10.11. Reverse Linked List II
- 10.12. Merge Two Sorted Lists
- 10.13. Merge k Sorted Lists
- 10.14. Reorder List
- 10.15. Copy List with Random Pointer
- 10.16. Sort List
- 10.17. Insertion Sort List
- 10.18. Check if a singly linked list is palindrome
- 11. Reverse - 翻转法
- 12. Binary Tree - 二叉树
- 13. Binary Search Tree - 二叉搜索树
- 14. Exhaustive Search - 穷竭搜索
- 15. Dynamic Programming - 动态规划
- 16. Appendix I Interview and Resume
Insertion Sort List
Source
- leetcode: Insertion Sort List | LeetCode OJ
- lintcode: (173) Insertion Sort List
Sort a linked list using insertion sort.
Example
Given 1->3->2->0->null, return 0->1->2->3->null.
题解1 - 从首到尾遍历
插入排序常见的实现是针对数组的,如前几章总的的 Insertion Sort,但这道题中的排序的数据结构为单向链表,故无法再从后往前遍历比较值的大小了。好在天无绝人之路,我们还可以从前往后依次遍历比较和交换。
由于排序后头节点不一定,故需要引入 dummy 大法,并以此节点的next作为最后返回结果的头节点,返回的链表从dummy->next这里开始构建。首先我们每次都从dummy->next开始遍历,依次和上一轮处理到的节点的值进行比较,直至找到不小于上一轮节点值的节点为止,随后将上一轮节点插入到当前遍历的节点之前,依此类推。文字描述起来可能比较模糊,大家可以结合以下的代码在纸上分析下。
Python
"""
Definition of ListNode
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
"""
class Solution:
"""
@param head: The first node of linked list.
@return: The head of linked list.
"""
def insertionSortList(self, head):
dummy = ListNode(0)
cur = head
while cur is not None:
pre = dummy
while pre.next is not None and pre.next.val < cur.val:
pre = pre.next
temp = cur.next
cur.next = pre.next
pre.next = cur
cur = temp
return dummy.next
C++
/**
* Definition of ListNode
* class ListNode {
* public:
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int val) {
* this->val = val;
* this->next = NULL;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param head: The first node of linked list.
* @return: The head of linked list.
*/
ListNode *insertionSortList(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode *cur = head;
while (cur != NULL) {
ListNode *pre = dummy;
while (pre->next != NULL && pre->next->val < cur->val) {
pre = pre->next;
}
ListNode *temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre->next;
pre->next = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode pre = dummy;
while (pre.next != null && pre.next.val < cur.val) {
pre = pre.next;
}
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre.next;
pre.next = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
源码分析
- 新建 dummy 节点,用以处理最终返回结果中头节点不定的情况。
- 以
cur表示当前正在处理的节点,在从 dummy 开始遍历前保存cur的下一个节点作为下一轮的cur. - 以
pre作为遍历节点,直到找到不小于cur值的节点为止。 - 将
pre的下一个节点pre->next链接到cur->next上,cur链接到pre->next, 最后将cur指向下一个节点。 - 返回
dummy->next最为最终头节点。
Python 的实现在 lintcode 上会提示 TLE, leetcode 上勉强通过,这里需要注意的是采用if A is not None:的效率要比if A:高,不然 leetcode 上也过不了。具体原因可参考 Stack Overflow 上的讨论。
复杂度分析
最好情况:原链表已经有序,每得到一个新节点都需要 次比较和一次交换, 时间复杂度为 , 使用了 dummy 和 pre, 空间复杂度近似为 .
最坏情况:原链表正好逆序,由于是单向链表只能从前往后依次遍历,交换和比较次数均为 , 总的时间复杂度近似为 , 空间复杂度同上,近似为 .
题解2 - 优化有序链表
从题解1的复杂度分析可以看出其在最好情况下时间复杂度都为 ,这显然是需要优化的。 仔细观察可发现最好情况下的比较次数 是可以优化到 的。思路自然就是先判断链表是否有序,仅对降序的部分进行处理。优化之后的代码就没题解1那么容易写对了,建议画个图自行纸上分析下。
Python
"""
Definition of ListNode
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
"""
class Solution:
"""
@param head: The first node of linked list.
@return: The head of linked list.
"""
def insertionSortList(self, head):
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
cur = head
while cur is not None:
if cur.next is not None and cur.next.val < cur.val:
# find insert position for smaller(cur->next)
pre = dummy
while pre.next is not None and pre.next.val < cur.next.val:
pre = pre.next
# insert cur->next after pre
temp = pre.next
pre.next = cur.next
cur.next = cur.next.next
pre.next.next = temp
else:
cur = cur.next
return dummy.next
C++
/**
* Definition of ListNode
* class ListNode {
* public:
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int val) {
* this->val = val;
* this->next = NULL;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param head: The first node of linked list.
* @return: The head of linked list.
*/
ListNode *insertionSortList(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode *cur = head;
while (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->next != NULL && cur->next->val < cur->val) {
ListNode *pre = dummy;
// find insert position for smaller(cur->next)
while (pre->next != NULL && pre->next->val <= cur->next->val) {
pre = pre->next;
}
// insert cur->next after pre
ListNode *temp = pre->next;
pre->next = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
pre->next->next = temp;
} else {
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.next != null && cur.next.val < cur.val) {
// find insert position for smaller(cur->next)
ListNode pre = dummy;
while (pre.next != null && pre.next.val < cur.next.val) {
pre = pre.next;
}
// insert cur->next after pre
ListNode temp = pre.next;
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre.next.next = temp;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
源码分析
- 新建 dummy 节点并将其
next指向head - 分情况讨论,仅需要处理逆序部分。
- 由于已经确认链表逆序,故仅需将较小值(
cur->next而不是cur)的节点插入到链表的合适位置。 - 将
cur->next插入到pre之后,这里需要四个步骤,需要特别小心!
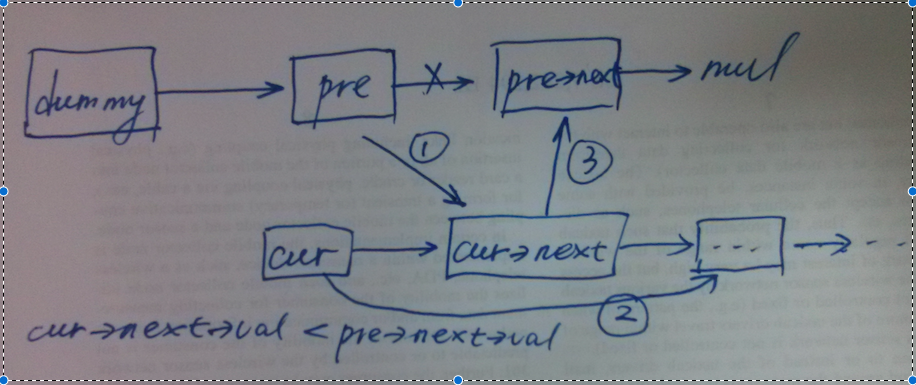
如上图所示,将cur->next插入到pre节点后大致分为3个步骤。
复杂度分析
最好情况下时间复杂度降至 , 其他同题解1.